Random Forest Regression
Random Forest Regression
Random Forest Regression is a supervised learning algorithm that uses ensemble learning method for regression. A Random Forest operates by constructing several decision trees during training time and outputting the mean of the classes as the prediction of all the trees.
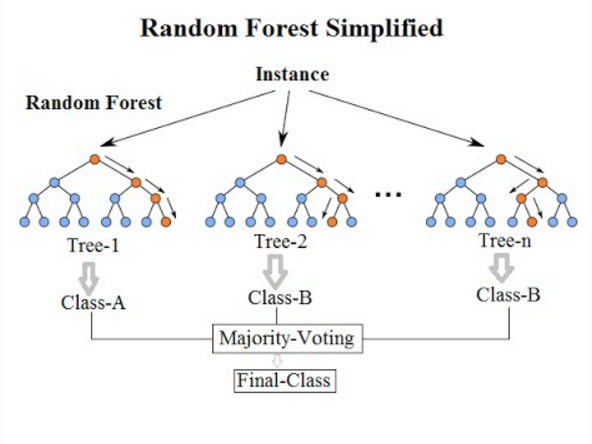
How does Random Forest work?
Random Forest regression works in the following way. Suppose you have a set of predictors (independent variables) and a target variable (dependent variable). The Random Forest regression model would then take a random subset of predictors and a random subset of data points from your data to grow a decision tree. The decision tree predicts the value of the target variable given the predictors.
This process repeats, each time with a new random subset of predictors and a new random subset of data points. The result is a "forest" of decision trees. Each tree gives you a prediction. The Random Forest model averages these predictions to deliver a final prediction that is robust and less prone to overfitting.
Python Implementation
Random Forest model can be implemented in Python using the RandomForestRegressor class in Scikit-Learn library.
Advantages of Random Forest Regression
-
Random Forest can handle large data sets with high dimensionality.
-
It can handle missing values and maintains accuracy for missing data.
-
The Random Forest algorithm develops a robust model because it takes the average of all the predictions of the decision trees.
-
The model does not suffer from the overfitting problem. The main reason is that it takes the average of all the predictions, which balances the biasness.
-
Random Forest regressor has a less variance then single decision trees. Hence, the model will not be very much affected by noise.
Disadvantages of Random Forest Regression
-
Complexity: Random Forest creates a lot of trees (unlike only one tree in case of decision tree) and combines their outputs. By default, it creates 100 trees in Python sklearn library.
-
Longer Training Period: Random Forest require much more time to train as compared to decision trees as it generates a lot of trees (instead of one tree in case of decision tree).
-
More Resources: The Random Forest algorithm is quick to use resources to the maximum extent. It requires more computational resources and it is less intuitive in case when we have a large collection of decision trees.
Scenario to use Random Forest Regression
Random Forest can be used in a variety of applications such as recommendation engines, image classification, feature selection, etc. It can be used for both regression and classification tasks. But it is mainly considered as a robust technique for regression and yet, not the first preference for classification tasks.
When it comes to regression, Random Forest is most useful with a large data set and complex problems. It is especially useful when the relationships between the variables are complex and difficult to tease apart with a linear model or other simple regression techniques.
Random Forest regression is a very powerful machine learning model and holds great promise for predictive modeling tasks. However, it should be used with proper care and attention to details since it is a more complex model and can be computationally intensive.