Decision Tree Regression With Python
Introduction
Decision Tree Regression is a machine learning algorithm that uses a decision tree model for predicting a continuous or categorical outcome. Like decision trees for classification, regression trees also split data based on feature values and assign predictions based on means or modes. However, instead of the output being a category, a decision tree regression gives an output that is a real value (or continuous value).
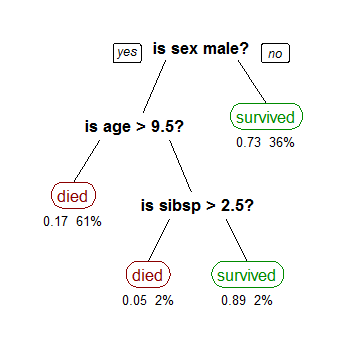
The Decision Tree Regression Model is created using two steps:
-
Splitting: This is a process of partitioning the data into subsets. Splitting is done on the basis of entropy and information gain.
-
Tree Pruning: In this process the unnecessary branches which have little role in decision making are removed. Generally, pruning is performed by removing the sections of the tree that provide little power to classify instances.
Python Implementation of Decision Tree Regression
The Python machine learning library, Scikit-Learn, supports decision tree regression through the 'DecisionTreeRegressor' class.
Here's a basic example of what python code might look like for decision tree regression:
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
# create a regressor object
regressor = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state = 0)
# fit the regressor with X and Y data
regressor.fit(X, Y)
Here, X and Y are the input and output values respectively.
Advantages of Decision Tree Regression
-
Ease to understand: Decision tree regressor models are visually intuitive and easy to interpret.
-
Requires less data preprocessing: It does not require normalization, dummy variables, etc.
-
Handles both continuous and categorical variables: Decision Tree Regressor is a type of algorithm that is capable of handling both types of variables.
-
Supports Multi-output: It is capable of predicting multiple outputs.
Disadvantages of Decision Tree Regression
-
Overfitting: Decision Tree Regressor sometimes creates over-complex trees that do not generalize the data well.
-
Instability: Small variations in the data might result in a completely different decision tree regression. This issue can be mitigated by using decision trees within an ensemble.
-
Possibility of bias: Decision-tree learners can create biased trees if some classes dominate.
Scenarios for usage
Decision Tree regression is used in several scenarios including:
-
When the relationship between features and the target variable is non-linear and complex.
-
When you need a predictive model that can be easily visualized and communicated.
-
When you need a model that can handle both categorical and numerical data.
-
In business decision making due to its easy to understand the logic behind the model.