Principal Component Analysis
Principal Component Analysis, essentially takes as input, the original dimensions, i.e. the m independent variables originally defined and then produces as output p new variables or dimensions. These are new extracted independent variables are the ones that explain the most variance of the dataset regardless of the dependent variables. The fact that we consider PCA as an unsupervised learning model, is the fact that it does not consider the dependent variable in the final model that it builds.
Functioning
The algorithm works on the basis of vector-matrix multiplication of the form 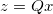 where
where 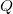 is a matrix and
is a matrix and  is a vector.
is a vector.
scalar * vector = another vector, same direction
matrix * vector = another vector, possibly different direction
So we could say, that PCA rotates the original input vectors.
Advantages
There are various benefits to using PCA:
- Decorrelates all the input data.
- Data is ordered by information content after the transformation
- Dimensionality Reduction (duh!)
Removing data does not always mean that the prediction ability will go down. In many cases the data is too noisy and dimensionality reduction proves to be an essential tool to smooth the data and generalize it.
RESEARCH REFERENCES
-
Principal Component Analysis and Factor Analysis
[Explains] The difference between Principle Component Analysis and Factor Analysis.