Ridge Classifier
Ridge classifier is a classification machine learning algorithm. It is a type of linear model that uses L2 regularization. Ridge Classifiers are essentially a regularized version of Linear Discriminant Analysis (LDA). When you have multi-class targets, a one-vs-rest scheme is used.
Basic Explanation
In simple terms, Ridge Classifier is a classification algorithm that uses L2 regularization to minimize the magnitude of the coefficients. This is done in order to prevent overfitting, which occurs when the model is overly complex and performs well on the training data but poorly on the test data.
Here is a diagram that represents the concept of overfitting, which Ridge Classifier tries to prevent:
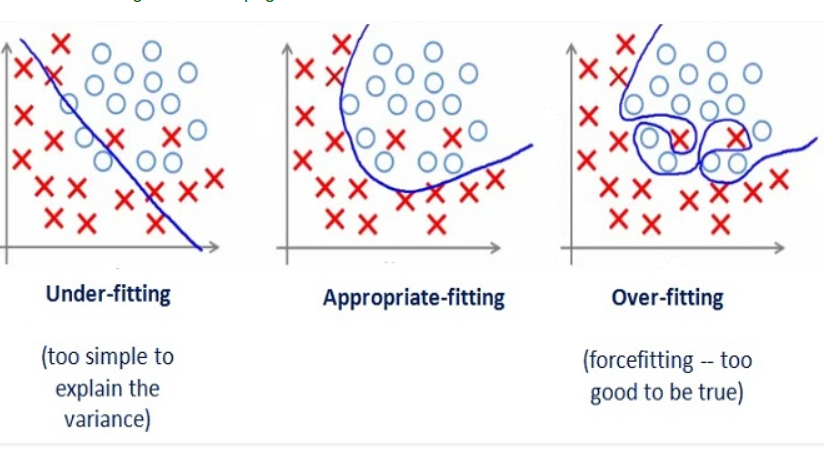
In the case of Ridge Classifier, each feature contributes to the decision function with a weight that is roughly proportional to its importance. It employs the so-called "ridge regression" as a base classifier, using a one-vs-rest scheme to deal with multi-class targets.
Python Example
Below is a simple example of a how to use the Ridge Classifier with Scikit-learn in Python.
from sklearn.datasets import make_classification
from sklearn.linear_model import RidgeClassifier
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
# Create a synthetic binary classification problem
X, y = make_classification(n_samples=1000, n_features=20, n_informative=15, n_redundant=5, random_state=1)
# Split dataset into training set and test set
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.3, random_state=1)
# Create Ridge Classifier
clf = RidgeClassifier()
# Train Ridge Classifier
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# Predict the response for test dataset
y_pred = clf.predict(X_test)
Advantages of Ridge Classifier
- Prevention of Overfitting: The Ridge Classifier's primary advantage is its ability to avoid overfitting through the use of L2 regularization.
- Handling Multicollinearity: Ridge Classifier can handle multicollinearity (high correlations between predictor variables) well.
- Efficiency: It works well even in situations where the number of variables is greater than the number of observations.
- Simplicity and Speed: It's generally faster than more complex machine learning algorithms.
Disadvantages of Ridge Classifier
- Not a Feature Selector: Ridge regression includes all predictors in the final model, so while it will shrink the coefficients of irrelevant variables close to zero, it will never fully eliminate them. This can lead to model interpretation problems if you have a high number of predictors.
- Sensitivity to High Variance: Ridge classifier can be sensitive to input features with high variances. This is because a feature with higher variance will influence the classifier output more. To circumvent this issue, we often standardize the input features so they all have the same variance.
Scenario to Use
Use Ridge Classifier when you have a multi-collinear dataset (multiple independent variables show some level of correlation with each other), or when you have many independent variables and you want to reduce the effect of overfitting.
It can be especially beneficial to use ridge regression when you're dealing with a problem where it's necessary to include all predictors, such as when you need to assess the effect of all predictors but don't necessarily care to create a sparse model.