Bagging Classifier
Introduction
Bagging, which stands for Bootstrap Aggregation, is a type of ensemble learning technique. The primary principle behind Bagging is to generate several subsets of the original data and then to train our model on each subset. The final output prediction is decided by averaging the individual predictions made by each model. In this write-up, we will provide a detailed explanation of the Bagging Classifier with a practical example in Python.
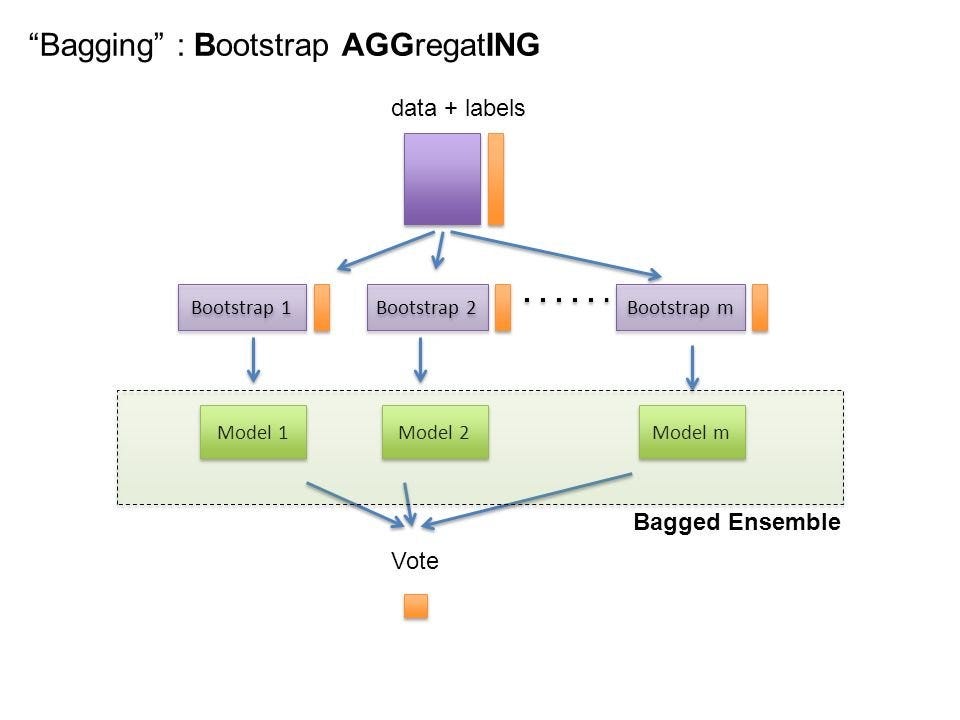
Applications of Bagging Classifier
Bagging classifiers are highly suitable for high-variance and low-bias models. This includes algorithms such as Decision Trees and Neural Networks.
Bagging is also great for tackling over-fitting issues. Over fitted models usually have a high variance, making Bagging an excellent choice to improve these models.
Python Implementation
Below is a short Python example on how to use the BaggingClassifier from sklearn:
from sklearn.ensemble import BaggingClassifier
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
# load iris dataset as an example
iris = load_iris()
X, y = iris.data, iris.target
# Train a KNN classifier
knn = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=3)
# Create a BaggingClassifier
bagging = BaggingClassifier(knn, max_samples=0.5, max_features=0.5)
# Fit the model to the data
bagging.fit(X, y)
# Make predictions
predictions = bagging.predict(X)
In the above code, we first imported the necessary libraries and loaded the iris dataset. We then defined a KNN classifier and a Bagging Classifier. The Bagging Classifier was then trained with the iris data, and predictions were made.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Bagging Classifier
Advantages:
- Handling Overfitting: Bagging helps reduce the variance error, thus helping complex models from overfitting the data.
- Parallel Training: Each model is built independently; thus, Bagging is naturally suitable for parallel execution.
- Handling Large Datasets: Bagging makes it possible to learn from a dataset that would otherwise be too large to fit in memory.
Disadvantages:
-
Bias Error: Bagging improves accuracy by reducing the variance term, but it remains ineffective for models with high bias errors.
-
Complex and Time-consuming: The Bagging Classifier has greater computational costs because it needs to build multiple models on different subsets of the dataset.
-
Predictability: As randomness is used for creating subsamples, the model can become slightly less interpretable than individual models.
When to use Bagging Classifier
- One common application for the bagging algorithm is to apply it to decision tree methods.
- It can be used when our data set has lots of features and instances, and probability of model overfitting is high.
- It can be applied to reduce the variance in a prediction by combining multiple decision trees to build an ensemble of trees.
Bagging, in the Random Forest method, helps to mitigate the variance problem with decision trees and also aids in avoiding overfitting.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Bagging Classifier is a powerful tool for increasing model performance by reducing variance error. Despite its disadvantages, its ability to learn from large datasets and mitigate overfitting is a major advantage in various practical applications.