Support Vector Machines In Python
Support Vector Machines (SVMs) are a type of classification algorithm, which is used in Machine Learning for classification and regression analysis. This supervised learning method is known for its kernel trick, allowing it to handle linear as well as non-linear data.
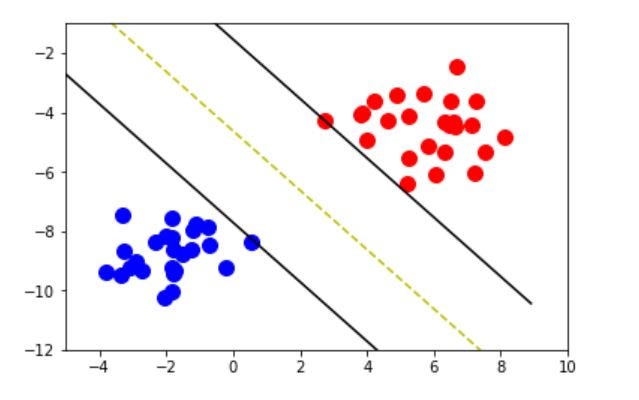
Understanding Support Vector Machines
The theory behind SVMs involves the concept of finding a hyperplane that separates the classes as much as possible. A hyperplane is a decision boundary that splits the data into classes. For a 2-dimensional dataset, the hyperplanes are simply lines, and for a 3-dimensional dataset, the hyperplanes are a plane; similarly, for higher-dimensional datasets, the hyperplane becomes n-dimensional.
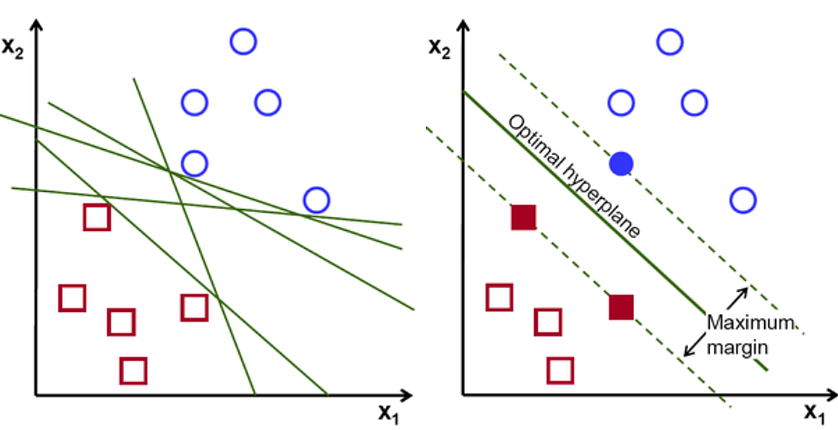
The distance between the hyperplane and the nearest data points from each class is called the 'margin'. The SVM algorithm's objective is to maximize this margin, to create the most efficient, reliable and generalized model. The data points that reside at the edge of the margin are called 'support vectors'.
Why Use SVMs?
- SVMs are effective in high-dimensional spaces.
- They are memory-efficient because they use a subset of training points (support vectors) in the decision function.
- They can classify complex, non-linear data thanks to the kernel function.
However, note that:
- SVMs do not perform well on large datasets because the training time could be cubic in the size of the dataset.
- They perform poorly if the dataset has more features than samples.
SVMs in Python
Python's Scikit-Learn provides built-in functions to use SVMs for both regression and classification tasks. A basic example of SVM-based classification using Scikit-Learn looks like this:
from sklearn import svm
from sklearn import datasets
# load iris dataset as an example
iris = datasets.load_iris()
X = iris.data
y = iris.target
# create a classifier
clf = svm.SVC(kernel='linear') # Linear Kernel
# train the model
clf.fit(X, y)
# predict a new example
new_sample = [[5.1, 3.5, 1.4, 0.2]]
print(clf.predict(new_sample))
This code trains an SVM classifier using the 'linear' kernel on the iris dataset, and makes a prediction for a new iris flower sample.
Advantages
-
Effective in high-dimensional spaces: SVM works well with even a large number of features as they compute the hyperplane using support vectors reducing computational complexity.
-
Works well on smaller cleaner datasets: They can perform better than other algorithms when the data set isn’t too large and parameters are correctly configured.
-
Versatile: When classifying, it uses a mechanism called kernels, which makes the method very versatile and able to handle different types of data structures.
-
Maximization principle implementation: It has solid theoretical foundations because its foundation comes from perturbation theory and statistical learning techniques, leading to solid algorithmic performances.
-
Avoid overfitting through regularization parameter adjustment: Overfitting typically happens when you have complicated decision boundaries; however, Adjustable regularization feature means we can reduce this risk significantly.
Disadvantages
-
Requires full labeling of input data: This is computationally expensive especially for larger datasets.
-
Doesn't work well with large dataset: The training time tends to increase exponentially with an increase in size of the dataset making SVMs inefficient for larger datasets.
-
Parameters tuning required: As free parameters need tuning such as the C parameter or kernel choice that may not be simple or intuitive without sufficient domain knowledge making efficient use tricky at times.
-
Inefficiency dealing with overlapping classes:If some classes overlap each other in several areas then separating them based on just one threshold value might result in errors while predicting data points close to these thresholds.
Appropriate Usage Scenarios
-
Face Detection: SVMc classify parts of images as face & non-face
-
Text Categorization: Commonly employed text categorisation techniques such as linear classifiers only offer effective solutions for linear separable sets but usage of boolean kernel rich context information can be captured , thus achieving greater accuracy levels .
-
Image Classification: Effectively used due to their ability working effectively in spaces higher dimensions .
-
Bioinformatics : Widely used application includes identifying people at cancer risks or protein remote homology detection .
Overall, SVM is ideally suited for situations where there's clear margin between separation within your classes/ objects under consideration identified by unique characteristics displayed by each category /type .
In summary, Support Vector Machines are a powerful technique for classification tasks, equipped with the ability to manage high-dimensionality data and with the flexibility offered by the kernel function.