Decision Tree Classifier
A Decision Tree is a simple but powerful machine learning technique that is mostly used for classification and regression tasks in machine learning. The decision tree algorithm tries to solve the problem by using tree representation. Each internal node of the tree corresponds to an attribute, and each leaf node corresponds to a class label.
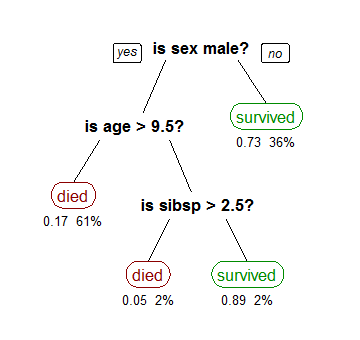
The topmost node in a Decision Tree is known as the root node, which learns to partition based on the attribute values. This process is performed recursively in a manner called recursive partitioning.
Building a Decision Tree:
The philosophy of Decision trees is to find those descriptive features that can help us differentiate the classes—in binary classification— or distinctive conditions in the class variable for the multi-class problems.
A decision tree is built top-down from a root node and involves partitioning the data into subsets that contain instances with similar values (homogeneous).
The following python code can be used to implement a Decision Tree Classifier:
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import cross_val_score
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
# Load data
iris = load_iris()
# Create decision tree classifier
clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=42)
# Train model
model = clf.fit(iris.data, iris.target)
In the above Python script, we start off by importing the necessary libraries. Then, we load the Iris dataset and finally create the Decision Tree Classifier and train the model using the fit method.
Advantages of decision trees:
-
Easy to understand: The Decision Tree algorithm is easy to understand, interpret, and visualize since it follows a clear, logical model.
-
Less data cleaning required: The algorithm requires less data cleaning compared to some other modeling techniques. It is not influenced by outliers and missing values to a fair degree.
-
Data type is not a constraint: It can handle both numerical and categorical variables.
-
Non-parametric method: Decision Tree is considered to be a non-parametric method, meaning that decision trees have no assumptions about the space distribution and the classifier structure.
Disadvantages of decision trees:
-
Overfitting: Over-complex trees do not generalize the data well, resulting in overfitting. This can be solved with techniques like pruning or setting the minimum number of samples per leaf.
-
Unstable to variations: Small variations in the data can result in a different decision tree. Hence they are usually used in an assembly (like Random Forest) for getting more robust predictions.
-
Biased trees: If some classes dominate, Decision Trees will create biased trees. So, it is recommended to balance out the dataset before building the decision tree.
Appropriate Usage Scenarios
Decision Trees are mostly used in classification problems. However, they are also fit for regression type tasks. They are particularly useful in the following scenarios:
-
Decision-making tasks: Given its transparent model, decision trees are useful for decision-making tasks like whether a borrower will default on a loan, whether to launch a new product, or what strategy to adopt in a game.
-
Feature selection: Decision Trees algorithms like Random Forests and Gradient Boosting can be used to rank the importance of the different features.
-
Medical diagnosis: Decision Tree algorithms are often used in the medical field for diagnosis of patients based on their symptoms or test results.
Conclusion:
Decision Trees are easy to understand, interpret and visualize. Although they are sensitive to fluctuations in data and are prone to overfitting, they can be powerful tools for exploring and understanding your data, especially when combined with ensemble methods.